Solar-Powered Lighting: The Technological Evolution from Past to Present
Today we live in a period where energy demand is rising rapidly, and the shift toward renewable energy sources is becoming more important than ever to meet that demand. Because lighting systems account for a significant share of global energy consumption, finding sustainable and efficient solutions in this field has become crucial. This is exactly where solar-powered lighting stands out: with its environmental and economic advantages, it is being adopted more widely every year.
The Development of Solar Energy and Photovoltaic Technology
The photovoltaic (PV) effect—converting sunlight directly into electricity—was first discovered in 1839 by the French physicist Alexandre Edmond Becquerel. Later, in 1883, American inventor Charles Fritts built the first photovoltaic solar cell, laying the groundwork for the technology. However, the panels produced at that time were extremely inefficient and not suitable for commercial use.
Modern high-efficiency solar panels entered our lives in 1954, when Bell Labs developed silicon-based solar cells. Initially used mainly for space research, this technology evolved over time and has become a critical part of global energy generation today.
The Role of Solar Lighting Today
Today, solar-powered lighting systems do more than reduce energy costs—they also provide a reliable solution in rural regions and underserved areas where grid electricity is unavailable or infrastructure is limited. These systems store energy throughout the day via photovoltaic panels and deliver uninterrupted lighting at night.
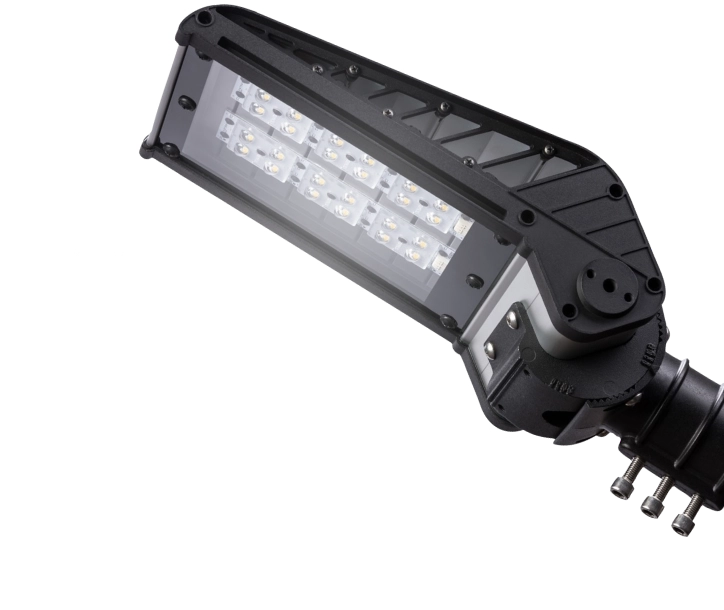
Next-generation solar lighting solutions are equipped with high-efficiency PV panels, long-life lithium batteries, motion sensors, and smart control systems. This prevents unnecessary energy consumption while increasing both efficiency and product lifespan. As a result, solar lighting is now used across a wide range of applications—from city streets to parks and gardens, from security lighting to smart-city projects.
Solar Panel Efficiency Today: The Latest Point in the Technology
In recent years, major advancements have been made in photovoltaic panel efficiency. High-efficiency panels currently available on the market can reach roughly 20% to 25% efficiency. Meanwhile, some research efforts and commercial solutions have achieved photovoltaic cell efficiencies above 40% in laboratory conditions.
One of the most notable examples is perovskite solar cells. These cells can be produced at significantly lower cost than traditional silicon cells, can exceed 30% efficiency, and are expected to become more widely used in the future. Bifacial solar panels are also gaining momentum. By capturing light from both the front and the back sides, they increase overall efficiency and generate more energy.
Finally, multi-junction (layered) solar cell technology is another innovative approach that boosts photovoltaic efficiency. By using layers designed to absorb different wavelengths of light, these cells can utilize a broader portion of the solar spectrum.
Future Expectations
As technology advances, AI-supported lighting control, wireless communication technologies, and improved battery management systems are making solar lighting solutions smarter and more durable. In the coming years, these systems are expected to be used more effectively in areas such as urban traffic management, security lighting, portable solar systems, and smart-city applications.
Aligned with energy-efficiency goals and sustainable development targets, solar-powered lighting will play an increasingly critical role in the future.
Get in Touch
For inquiries about our products, technical support, or partnership opportunities, please click the button below to access our contact form. Let’s illuminate your projects together!




Get in Touch
For inquiries about our products, technical support, or partnership opportunities, please click the button below to access our contact form. Let’s illuminate your projects together!